
What is Putaway in Warehousing? Meaning, Process, and Best Practices
Table of Contents
What is Putaway in Warehousing?
In warehousing, efficiency begins the moment goods enter your facility. One process that quietly defines how smoothly everything else runs — from inventory accuracy to order fulfillment speed — is putaway.
Putaway refers to the systematic movement of received goods from the inbound area to their designated storage locations. It ensures every item is stored in the most logical, accessible, and space-efficient manner. Though often overlooked, it’s one of the most crucial steps in warehouse management — bridging the gap between receiving and picking.
You May Also Like to Read: What is Traditional Warehousing
Why Putaway Matters in Warehouse Operations?
A warehouse’s productivity hinges on how well it organizes and manages its space. Without a structured putaway process, items pile up in receiving docks, aisles get congested, and order pickers waste time searching for misplaced stock.
Efficient putaway helps:
- Maintain real-time inventory accuracy
- Improve space utilization
- Reduce handling time and operational costs
- Enhance worker productivity and safety
- Speed up order fulfillment cycles
Essentially, putaway transforms a warehouse from a chaotic storage site into a data-driven logistics ecosystem where every item is exactly where it should be.
The Step-by-Step Putaway Process in Warehouse
Let’s break down how putaway works in a well-structured warehouse:
1. Receiving and Verification
Goods arrive at the inbound dock and are checked against purchase orders or ASNs (Advanced Shipping Notices). The accuracy of this step is critical because it sets the foundation for the entire inventory record.
2. Identification and Labeling
Every item or pallet receives a barcode or RFID tag that captures its SKU, batch, quantity, and condition. This enables seamless digital tracking within the Warehouse Management System (WMS).
3. Location Assignment
Based on product dimensions, weight, and demand frequency, the WMS suggests an optimal storage location. This is where strategy and software intelligence come together — ensuring the item’s future movement is as efficient as possible.
4. Transport to Storage Area
Warehouse operators move goods via forklifts, pallet jacks, or conveyors to the designated locations. Clear signage, optimized routes, and automation (like AMRs) make this step faster and safer.
5. Inventory Update
Once the item is stored, the WMS automatically updates its location in the system. This allows warehouse teams to know the exact bin, rack, or slot where an item resides — crucial for accurate picking later.
Types of Putaway Strategies
The putaway strategy defines how and where goods are stored. Different operations demand different approaches:
| Strategy | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Location Putaway | Each SKU is assigned a permanent storage spot. Simple but may waste space. | Predictable, low-SKU warehouses |
| Dynamic Putaway | Storage locations are allocated in real time based on space and proximity. | High-SKU or fast-moving operations |
| Zone Putaway | Warehouse is divided into functional zones; items are placed based on type, size, or handling needs. | Multi-category storage environments |
| Direct Putaway | Items are transferred directly from receiving to final storage without staging. | Time-sensitive or cross-docking setups |
| Class-Based Putaway | Items are grouped by class (e.g., A-B-C analysis) and stored based on demand frequency. | Demand-driven warehouses |
Modern WMS software often combines multiple strategies to adapt dynamically to volume fluctuations and seasonal demand.
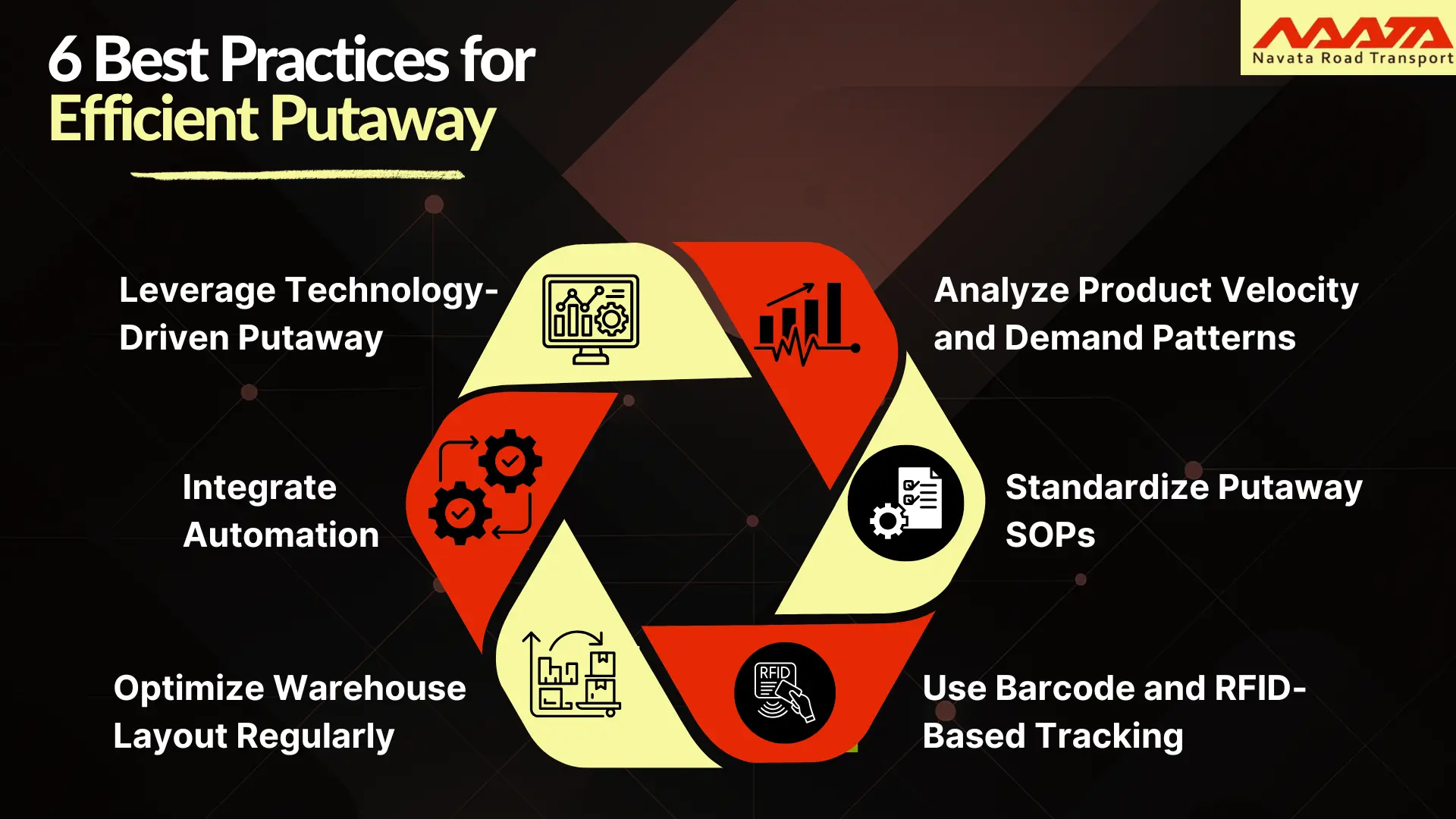
Best Practices for Efficient Putaway
Leverage Technology-Driven Putaway
A modern Warehouse Management System (WMS) removes manual judgment from putaway by using real-time data, item attributes, and space availability to recommend optimal storage locations. Intelligent slotting ensures goods are placed where they can be accessed fastest, reducing errors, congestion, and future picking inefficiencies.
Analyze Product Velocity and Demand Patterns
Putaway decisions should be guided by SKU velocity, order frequency, and seasonality. High-moving items stored closer to dispatch zones significantly reduce picker travel time and handling effort. Velocity-based putaway enables faster fulfillment cycles and prevents bottlenecks during peak demand periods.
Train Teams and Standardize Putaway SOPs
Even the most advanced systems fail without disciplined execution. Clearly defined SOPs ensure consistent putaway methods across shifts and locations. Regular training minimizes misplacement, improves safety, and ensures warehouse staff fully leverage WMS-guided workflows instead of relying on habit or intuition.
Use Barcode and RFID-Based Tracking
Digitized identification through barcode or RFID scanning ensures every movement during putaway is recorded instantly. This eliminates manual data entry errors, improves location accuracy, and maintains real-time inventory visibility—critical for multi-SKU, high-volume, or multi-client warehouse environments.
Review and Optimize Warehouse Layout Regularly
Putaway efficiency declines when layouts remain static while demand changes. Regular re-slotting based on order trends, SKU growth, and seasonality ensures space is always optimized. Continuous layout optimization reduces travel distance, improves space utilization, and sustains long-term warehouse performance.
Integrate Automation Where Volume Demands It
Automation such as Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), conveyors, and automated storage systems accelerates putaway in high-throughput environments. By reducing manual handling and labor dependency, automation improves consistency, supports scalability, and enables warehouses to manage growing volumes without operational strain.
Common Challenges in the Putaway Process
Even efficient warehouses face recurring bottlenecks such as:
- Congested receiving areas during peak hours
- Manual data entry errors leading to misplaced stock
- Lack of visibility into real-time storage space availability
- Unoptimized routing, causing longer travel time for forklifts
Overcoming these requires a blend of layout redesign, WMS integration, and operator training — not just more manpower.
The Role of WMS in Modern Putaway
A Warehouse Management System transforms putaway from a manual task into a data-driven operation.
Modern WMS platforms:
- Automatically assign optimal storage based on item attributes
- Provide visual maps for real-time slot tracking
- Track labor productivity per putaway cycle
- Integrate with IoT sensors for temperature- or weight-sensitive goods
This combination of visibility, intelligence, and automation is what defines next-generation warehouse efficiency.

Read More About: Benefits of Warehouse Automation
Conclusion
Putaway is not just about storing items — it’s about strategic organization that shapes every downstream activity in a warehouse. A warehouse that gets putaway right ensures faster order fulfillment, better accuracy, and maximum use of space.
As eCommerce and supply chain complexity rise, businesses must rethink their putaway processes — from manual movement to smart, data-driven storage optimization.
Thank You For Reading: What is Putaway in Warehousing? Meaning, Process, and Best Practices
Powered By 360Presence






