Artificial Intelligence in Logistics Industry
Table of Contents
What Exactly is Artificial Intelligence in Logistics?
AI refers to software that mimics human learning and decision‑making. In logistics, it collects real‑time data—from barcode scans, telematics, weather feeds, and customer clicks—and turns it into actions such as forecasting demand, routing trucks, or guiding warehouse robots. Unlike traditional automation, AI keeps learning, so its recommendations improve every day.
Artificial Intelligence in the logistics industry is no longer a futuristic idea—it is the engine that powers today’s most efficient supply chains. From same‑day deliveries to predictive inventory planning, AI helps logistics companies move goods faster, cleaner, and at lower cost.
In this guide, you’ll learn what AI means for logistics, the main use cases, the benefits and hurdles, and where the technology is heading next—all in clear language you can share with your team.

You May Also Like To Read: 7 Best Supply Chain Technology Trends & Innovations
Why AI Matters Right Now in Logistics?
- Cost pressure is rising. Fuel, labor, and warehousing costs keep climbing, forcing logistics providers to do more with less.
- Data is exploding. IoT sensors, GPS trackers, and e‑commerce platforms generate terabytes of fresh data every hour; AI is the only practical way to use it all.
- Customer expectations are sky‑high. Two‑hour delivery windows and full order visibility are becoming the norm.
A 2025 survey found 52 % of logistics companies have already cut costs after adopting AI, while 70 % report higher customer satisfaction. Meanwhile, half of global supply‑chain leaders plan to roll out generative AI.
You May Also Like To Read: 10 Major Benefits of Internet of Things (IoT) on Supply Chain Management
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Logistics
Warehouse Automation & Robotics
AI‑directed robots handle picking, sorting, and palletizing faster than manual crews. Amazon has deployed more than one million robots, now assisting 75 % of its deliveries. Vision‑guided systems identify items, avoid obstacles, and learn the best grip points, boosting productivity and reducing injuries.
Predictive Demand & Inventory Planning
Machine‑learning algorithms analyze past sales, holidays, and even social‑media buzz to forecast demand up to 40 % more accurately than legacy models. This precision lowers stock‑outs and excess inventory, freeing up cash.
Smart Routing & Fleet Management
AI crunches traffic patterns, fuel prices, and load weights to suggest the fastest, greenest route in real time. Fleet operators that use AI have slashed fuel consumption by 15 % and trimmed delivery times by up to 30 %.
Real‑Time Visibility & Customer Service
Natural‑language chatbots answer shipment queries instantly, while computer‑vision tools track package condition at each touchpoint. The result is fewer “where‑is‑my‑order” calls and happier customers.
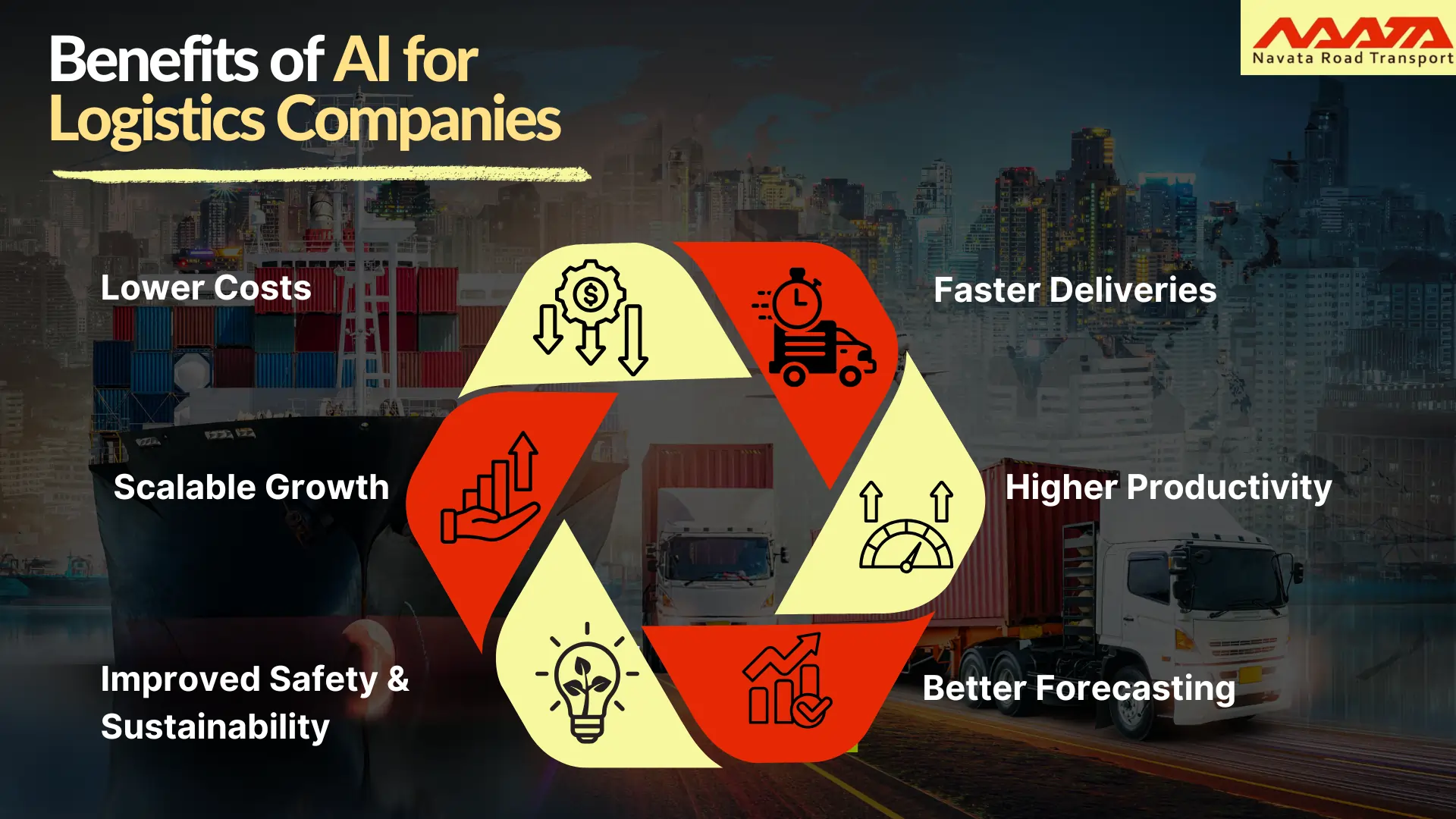
Benefits of AI for Logistics Companies
- Lower Costs: AI optimizes routes, labor, and warehouse space, cutting operating expenses by 10–15 %.
- Faster Deliveries: Algorithms cut empty miles and shorten pick‑pack times, improving on‑time‑delivery rates by up to 25 %.
- Higher Productivity: Robotic process automation (RPA) saves an average 10 hours per worker per week.
- Better Forecasting: Demand‑planning AI reduces forecast errors by as much as 40 %, stabilizing inventory and cash flow.
- Improved Safety & Sustainability: Predictive maintenance lowers breakdowns, and smarter routing reduces carbon emissions by 15 %.
- Scalable Growth: Cloud‑based AI tools let even mid‑size carriers tap data science without hiring a full research team.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Challenge | Why It Happens | Practical Fix |
Data Quality | Disparate systems store data in different formats. | Standardize data fields and set up real‑time APIs before training models. |
Talent Gap | AI skills are scarce in logistics. | Upskill existing staff and partner with AI vendors for phased rollouts. |
Change Management | Workers fear job loss. | Communicate early wins, create new “robot supervisor” roles, and involve teams in design. |
Steps to Implement AI in Logistics
- Audit Your Data: Identify high‑value data streams (orders, telematics, WMS logs).
- Pick a Pain Point: Choose a clear, measurable problem—e.g., late deliveries or stock‑outs.
- Run a Pilot: Partner with a tech provider; aim for a 90‑day proof of concept.
- Measure & Iterate: Track KPIs such as cost per delivery or forecast accuracy.
- Scale & Integrate: Extend successful pilots across regions, then connect them to your TMS/WMS.
- Build a Culture of Learning: Offer AI literacy workshops so teams can spot new use cases.
Future Trends to Watch (2025‑2030)
- Generative AI for Dynamic Planning: Large language models will write instant “what‑if” scenarios for weather events and port strikes.
- Autonomous Trucks & Drones: Self‑driving pilots are expanding on controlled highways in the U.S., Europe, and parts of Asia, with a CAGR of 39 % forecast for autonomous vehicles in logistics.
- Green Logistics Optimization: Carbon‑aware AI will adjust routes to minimize emissions and help firms meet net‑zero targets.
- AI‑Enabled Circular Supply Chains: Advanced analytics will track reverse‑logistics loops, improving refurbish‑and‑resell programs.
- Edge AI & 5G: Processing data on the truck or robot will cut latency, making real‑time decisions even faster.

You May Also Like To Read : 8 Proven Technologies in Logistic Sector for High Performance
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is rewriting the playbook for logistics—from the inside of a warehouse to the last mile of delivery. Companies that act now can slash costs, boost service, and future‑proof their operations. Those that wait risk falling behind faster than a missed next‑day shipment. Start small, learn quickly, and scale what works—the road to AI‑powered logistics is open and ready.
Thanks For Reading : Artificial Intelligence in Logistics Industry
Powered By 360Presence
Artificial Intelligence in Logistics Industry Artificial Intelligence in Logistics Industry



