Automation In Supply Chain Management, Logistics And Road Transport – The Benefits
Table of Contents
Introduction of Automation in Supply Chain Management
The global supply chain industry is an ever evolving industry. With the growing integration of advance Information Technology in logistics and road transportation, supply chain industry is constantly re- inventing itself at a rapid pace. Technological support helps to streamline operations in long run.
With regard to logistics management, it is imperative to make sure all items are stored, transported and delivered properly and efficiently. Technological solutions become vitally important here, and play a key role in ensuring efficiency at all levels.
Automation in supply chain management processes considerably helps to enhance efficiency in the transportation companies, and resultantly has a significant impact on bottom lines. The automation processes not only help achieve better profit margins, there are a several other benefits to it too. Bringing automation into the warehouse and distribution channels is of great advantage to all parties concerned.

Automation and its Benefits
“Process Automation” is the new buzzword. Advantages of process automation have wooed over businesses, which are increasingly integrating it into their transportation logistics to make operations easier and smoother. The ‘lights-out’ type of automated warehouses have gained popularity, and are a growing option wherever labour costs are too high, and there is a priority need for information arbitrage and speed of fulfilment.
The integration of latest technology ensures that all tasks and operations are highly coordinated, to enable a smooth transition from placement of the original order to fulfilment and delivery to the customer. With end to end automation of the entire supply chain, beyond individual task automation processes, the logistics managers are less stressed with everyday processes, and can concentrate more on making sure that the supply chains are bringing in the optimum best at any given point
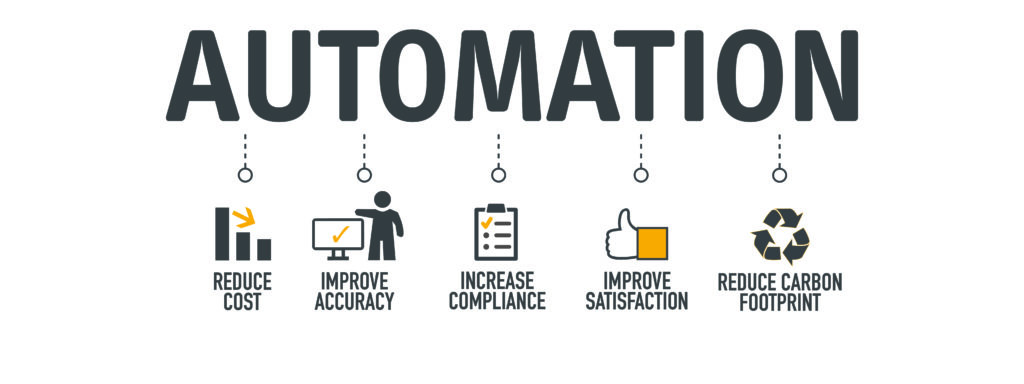
Automation in Supply Chain Management & Logistics
Automation can be understood as automatic control. It is the use of various control systems for operating equipment, such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers and heat treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering and stabilization of ships or aircraft, and other applications, with the least amount of human intervention.
Some of these processes are completely automated, which means they require no human intervention.A major and the most significant benefit of automation is that it saves labour. Also, it contributes in saving of energy and resources. Automation holistically improves quality, accuracy and precision in the overall process, thereby enhancing efficiency in the big picture.
For instance, automation decreases labour time spent on manual entry, helps bring efficiency in the process of planning the movement of goods in the supply chain logistics, it helps in cost reductions, and decreases overall errors, thereby leading to customer satisfaction and enriching customer experience.
In The Transportation Management System, TMS, Logistics automation involves all the automation features that are at its disposal, for the proper management of the transportation and freight sector. Automation in the logistics industry primarily is the reduction in the manual entry of the freight shipment data, and the option of automatic retrieval options in the procurement of transportation for the freight.
Image – Automation in Supply Chain Management
Logistics Automation and its Advantages
1) Enhanced Accuracy and Reduction in Costly Errors:
Automation in Logistics managements protects the system from errors of entry and calculations which prove expensive. Automation features, such as integration to various services via number of integrated system, and access to personalised data, and automatic accounting of entry of fuel charges, expenses and accessories, all of this data is accurately managed through automation, without stressing over accidentally keying in incorrect information.
Often, these manual data entry errors lead to increased shipping costs, which result in paying for shipping twice, or paying a higher freight rate due to erroneous data entry.
2) Transportation Mode Choice and Real Time Freight Rates:
Automation helps to keep track of the trending rates as per the current market rate, with the help of all data analysis, and constantly updates to the latest rates on the Internet based platforms. This helps to tackle the transportation cost fluctuations in the logistics industry.
This removes the issue of theoretical savings, and only focuses on hard rates of interest based on live, vendor neutral access to real-time market rates, thereby increasing the accuracy of cost analysis.
Such accuracy is of great advantage when one has to consider selecting from multiple carriers, based on cost, transit time, and insurance. Automation in Supply Chain Management empowers one to make the best choice for a specific shipment, thereby saving money in the long run
3) Improved Customer Service:
Losing valuable customers, bad reviews, poor customer retention rate are all bad for any business.Automated tracking systems and notifications help to keep the customer and the owner informed and thus enrich the customer experience positively.
Logistics automation features like, on-the-go freight tracking, automated pick-up, maintained insurance and freight accounting built as per the custom specifications, empower the customers and the owners with information with regard to the exact freight cost and the time as to when the freight will arrive at its destination, through automatic notifications.
4) Accurate Real-Time Freight Data Analysis:
Access to accurate real time freight data, and its ability to run reports, empowers the company and helps in making better business decisions, based on trends and history. For example, if a company offers good transportation service in less cost but often delivers the product later than scheduled, it brings in bad customer service reviews.
Momentary saving of money on freight transport is just a short term benefit. In the long run, bad customer service reviews eventually translate into heavy losses that hurt the business when the company is unable to gain new customers and loses valuable customers.
Automation in Supply Chain Management Brings Ad-hoc Benefits
1) Safe Work Environment:
Automation in Supply Chain Management processes accurately assess and monitor the operations, thereby ensuring safety. For instance, in the warehouse temperatures reaching -38 degrees Fahrenheit are not a safe work environment. Automated robotics or automated vehicles monitor the temperatures and help create safety in terms of human workforce and general safety.
Thus, people working can safely take on higher-level responsibilities in the management and maintenance of these automated systems. Automation is definitely changing the overall work situations and making it more favourable for the people involved in it.
2) Improved Inventory Management:
It is important to keep products in the proper climate controlled environment, to reduce the risk of product getting spoiled or degraded, specially so in the cold supply chain. By employing just-in-time fulfilment strategies, warehouses do not have to plan the orders too much in advance. Instead, they can make more frequent, yet planned reasonably in advance freights, for the products that are bound to spoil early.
This reduces the risk of running out of stock or the risk of facing the challenge of stock wastage.Automated systems can make proper freight planning and limiting products, thus making their sustainability more efficient. This prevents warehouses from holding products for too long and risking expiry, leading to product waste, or worse, reaching consumers late, and becoming a safety concern.
3) Reduced Costs:
Effective space utilization helps in cost reduction as there is less area to cool and often fewer refrigeration units are needed. This naturally leads to additional energy and cost savings. Lowering the number of interior lights, the energy savings made possible by using storage and retrieval machines fitted with regenerative braking systems lead to further cost reductions.
These mechanisms allow companies to store surplus braking energy share among all the machines using power from the same grid. Hence automation greatly helps to conserve energy and thereby lead to optimization of all resources, and lower the running costs considerably.
Conclusion
Automation in Supply Chain Management has completely reinvented the logistics sector. Higher efficiencies, powerful tools, better and safer work environments and increased gains in terms of profit and lowered running costs has revamped the logistics industry. Automation is a constantly self-updating process that will keep evolving and changing the Logistics and Supply Chain Management sector, empowering it with better systems every day.
Blog: Automation In Supply Chain Management, Logistics And Road Transport – The Benefits
Powered By 360Presence
Leave a Replay
Automation in Supply Chain Management Logistics automation logistics and road transport Automation in Supply Chain Management Logistics automation logistics and road transport Automation in Supply Chain Management Logistics automation logistics and road transport




